Zero-dose children* are those that have not received any routine vaccine. In the Western Pacific Region, the number of zero-dose children increased by 45%[1] from around 960 000 in 2019 to 1.4 million in 2021. Globally, there were around 18 million zero-dose children in 2021 and 78% of these children lived in only 20 countries, including the Philippines (1 million) and Viet Nam (187 000)[2].
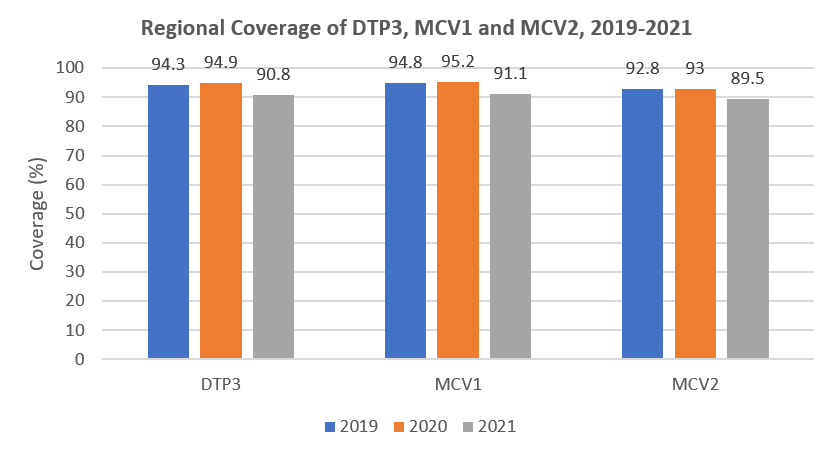
Coverages of the third dose of diphtheria, tetanus toxoid, pertussis vaccine (DTP3) and the first and second doses of measles-containing vaccine (MCV1, MCV2) also decreased between the years 2019 and 2021. See Figure 1.
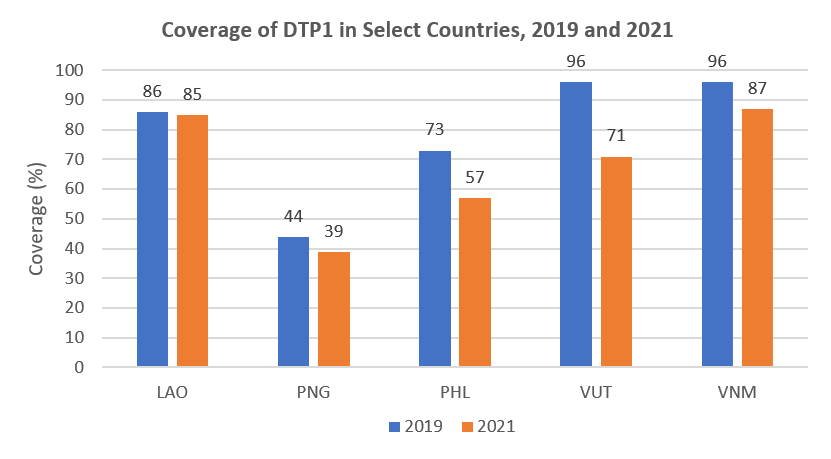
Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Vanuatu, and Viet Nam had the lowest coverage of first dose of DTP1 (DTP1), which translates to a high number of zero-dose children in 2021[2]. DTP1 coverage for these countries all decreased in 2019 and 2021 as shown in figure below.
The COVID-19 pandemic along with its associated disruptions (i.e., school closures, postponement of immunization campaigns and travel restrictions) and needed vaccination response have strained the health systems which contributed to decreased childhood immunization coverage in some countries in the Region. Low immunization coverage increases the risk of severe diseases for children and may result in outbreaks if the ideal coverage rate of 95% for all routine childhood vaccines is not reached.
Lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic and response highlight the need to strengthen primary health care through multi-sectoral collaboration and integration of health services. Efforts to integrate COVID-19 vaccination into routine immunization services should be prioritized and investments made for COVID-19 response should be leveraged to strengthen routine immunization delivery mechanisms, cold chain capacity and information systems.
*In this analysis, zero-dose children are those who lack any dose of DTP
[1] WHO/UNICEF Electronic Joint Reporting Form (eJRF) on Immunization
[2] WHO/UNICEF Estimate of National Immunization Coverage (WUENIC), July 2022